But that's not all. In addition to fiber, peas are full of plant proteins (they have about 5 grams per 100 grams of total weight). Proteins are what give your body strength, take care of muscles, aid in tissue repair, and make you feel full after a meal. That's also why a plate of rice fills you up less than a plate of rice with peas. Peas, so to speak, lock satiety into your stomach and don't let you search for chocolate in the drawer half an hour later.
In folk medicine, peas have been used for centuries as food that soothes the stomach and strengthens the blood. Although our ancestors didn't know words like glucose or oxidative stress, they knew that something worked. And science confirms this today.
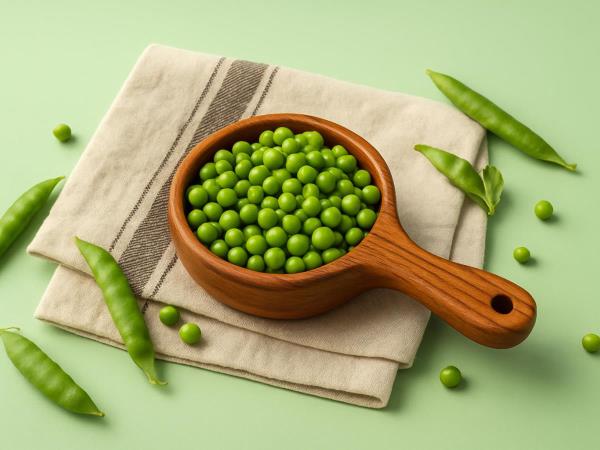
Why do peas make you feel fuller than half of other vegetables?
There is no magic here, just a very simple mathematical trick of nature. When you eat foods high in fiber and protein, your stomach stretches more slowly but more evenly, and your body sends signals to your brain that the food needs to be digested thoroughly and slowly. This means that the feeling of fullness can last up to 3 hours, as confirmed by a study at Stanford University in 2020, which tracked over 1200 people.
And here comes another important number: glycemic index (GI). This is the number that tells us how quickly food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI make you feel full quickly, but the effect fades just as quickly. Foods with a low GI work more gently and don't cause rapid mood swings, hunger, or fatigue. Peas have a GI of about 22-30, which is extremely low.
For comparison:
- white bread has a GI of 75-80,
- white rice GI 70,
- potatoes around 65.
So, peas are by no means just a side dish. In fact, they are one of the most stable and energy-balanced foods you can include in your diet.
Why were peas once considered food for strong people?
Our grandparents often said that peas are what gives you strength. In folk records from the early 20th century, you’ll find recommendations that pea soup should be given to young boys doing hard physical labor because it strengthens muscles and blood. Today we know this expression (strengthens the blood) was connected to the fact that peas contain a lot of vitamin K, which is important for bone health and normal blood clotting.
Vitamin K is what helps our immune system function more decisively and allows us to become less fatigued. Even though we might think it's just a vitamin found in pods, research from 2022 showed that adequate vitamin K intake reduces the risk of fractures in older individuals by 27%. That's quite a lot, considering that on average, seniors over 60 often suffer hip fractures...
Peas also contain vitamin C (about 40 mg of vitamin C per 100 g), which is half of your daily needs. Vitamin C is important not just for the immune system but also helps with collagen production, which everyone needs especially after the age of 40.
But why are peas so often overlooked?
Because they're too ordinary. And because we don't know how to prepare them in a way that excites us. Peas are a simple vegetable that we often cook only one way and then wonder why we're not interested.
When, in 2021 during the coronavirus pandemic, many people started cooking at home, sales of frozen peas in Europe increased by 34%. Why? Because they’re cheap, useful, and long-lasting. Yet at the same time, most people admitted they didn't really know what to do with them.
That's a shame because you can fry peas, bake them, blend them into soup, add them to salads and risottos, or use them as a main dish. And what's even more interesting, research from 2024 shows that cooking between 120 and 160 degrees increases the availability of antioxidants by 11-19%.
Are peas really the healthiest vegetable?
Nutritionists are cautious here, but the facts speak for themselves. Nutritionists don’t like to declare outright winners. Even with peas, they are reserved, saying each vegetable has its benefits. But if you had to make a list of vegetables most useful for people with unstable blood sugar, excess body weight, digestive problems, or a weak immune system, peas would be at the very top.
Why? Because of the combination:
- fiber,
- protein,
- vitamins,
- antioxidants,
- low glycemic index,
- affordable price in stores.
That’s a rare combination. So rare, in fact, that if a new product with such properties were launched in the marketing world, it would be sold at a premium price.
Our grandmothers knew how to make pea soup, which was a real energy bomb, but everyone took it for granted. But looking with today’s eyes, it was a soup that stabilized sugar, provided protein, filled you up, warmed you, and cleansed your digestive system.
It's worth remembering: fried peas are more filling than boiled peas.
It sounds incredible, but it’s true. When you quickly saut{-15447} peas with a spoon of olive oil, add some garlic and lemon zest, the fiber softens slightly, and the proteins are released more quickly during digestion. This was also confirmed by a study from Tokyo in 2020.
Garlic, which in combination acts as a natural antibiotic, provides extra antibacterial protection. Lemon zest adds antioxidants, which slow down cell aging.
How peas help in the real world
During the first wave of the pandemic, the British massively bought frozen peas because they were cheap, nutritious, and long-lasting. The government at the time even recommended legumes as the optimal food for a crisis. Sales increased by more than 40%.
In a report on nutrition trends published by the European Food Safety Agency, peas are listed as one of the three most recommended legumes when transitioning to a more plant-based diet. They are praised for their exceptional nutrient-to-price ratio.
So, in a time when we are facing high prices, fatigue, stress, quick meals, and poor eating habits, peas are an almost laughably simple answer. They’re cheap, accessible, nutritious, kids know them, adults sometimes forget them, but they work...
And they work better than you might think.







 Would you like to be informed about news on the website?
Would you like to be informed about news on the website?

